Example (zip.sas), data from 195 subjects in a prospective longitudinal survey are analyzed. Criminal offense convictions were recorded annually beginning for boys from age 8 through age 32. The analysis begins with Program 1 (below). The resulting output and graphs follow. Extra zero probability in the model is specified using the IORDER statement. IORDER 1; indicates that we'll model the probability of extra-Poisson zeros with a linear function common to all of the groups.
Program
1: Three-group ZIP model, cubic trajectories.
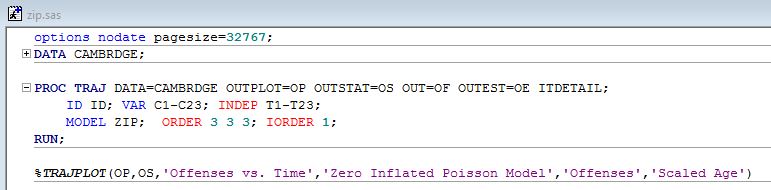
Output 1:Three-group ZIP model, shared linear zero inflation probability.
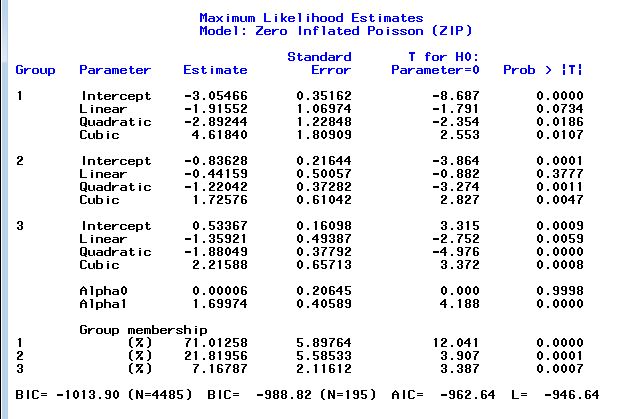
Graph 1: Sample average and predicted trajectories.
The model appears satisfactory so we'll just try adding the risk factors without using start values.
Program
2: Three-group ZIP model, cubic trajectories with risk factors.
Output 2: Three-group model with risk factors.
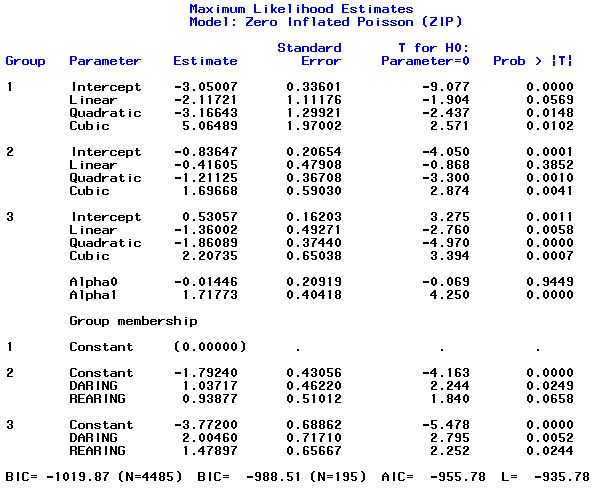
Daring and rearing are 0/1 variables. Daring is 1 for high levels of daring behavior observed in the subject. Rearing is 1 for high levels of poor rearing practices by the parents. The results show that both high levels of daring behavior and poor rearing increase the likelihood of belonging in the higher offending groups (insufficient evidence that poor rearing is more frequent in the middle group in this example, p=0.0658). (zip.sas)