Assignment 2
1. Exploring loss functions
1.1. Fitting a voxel grid (5 points)
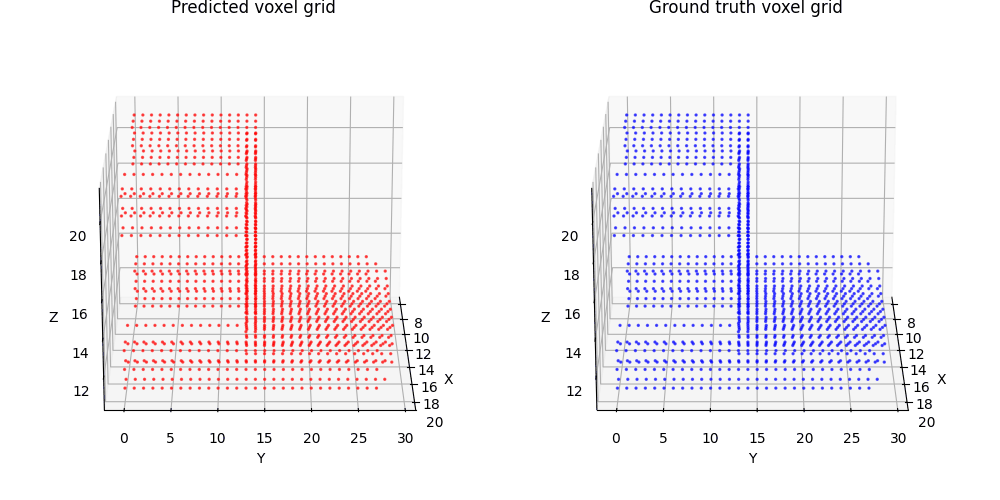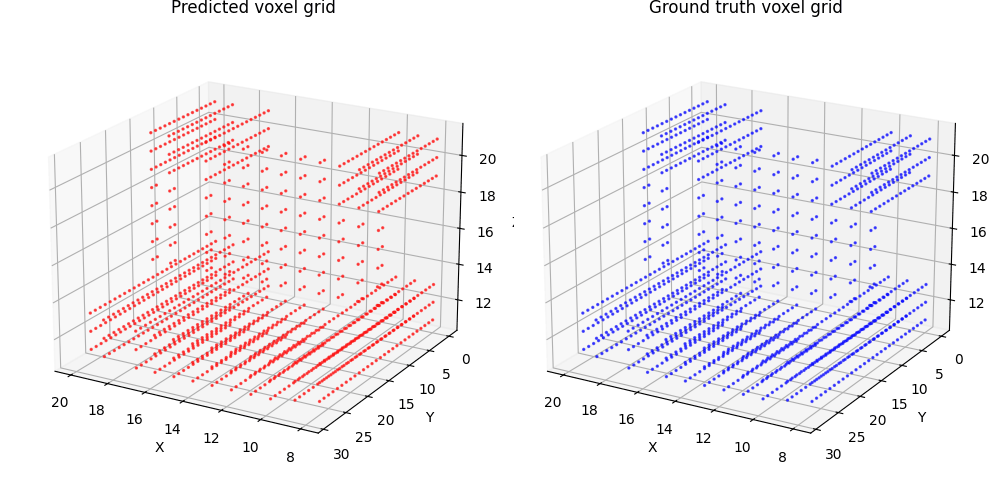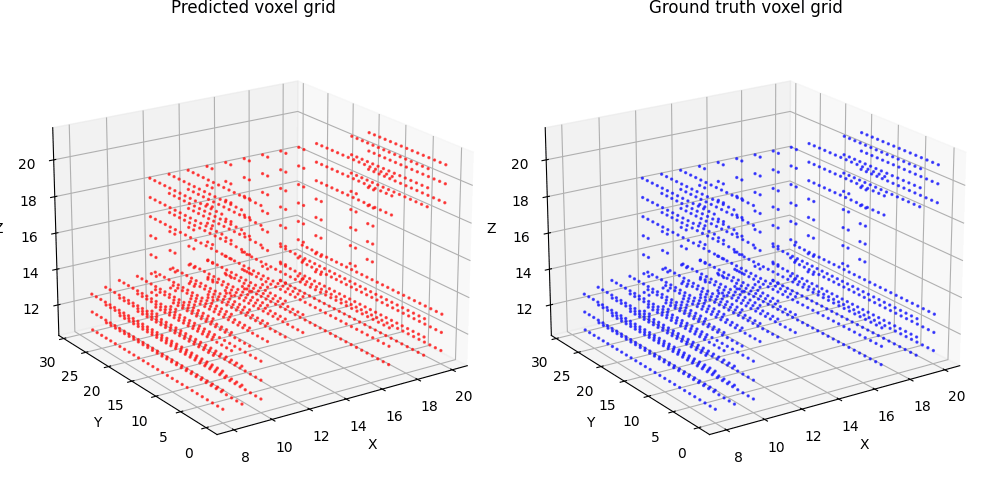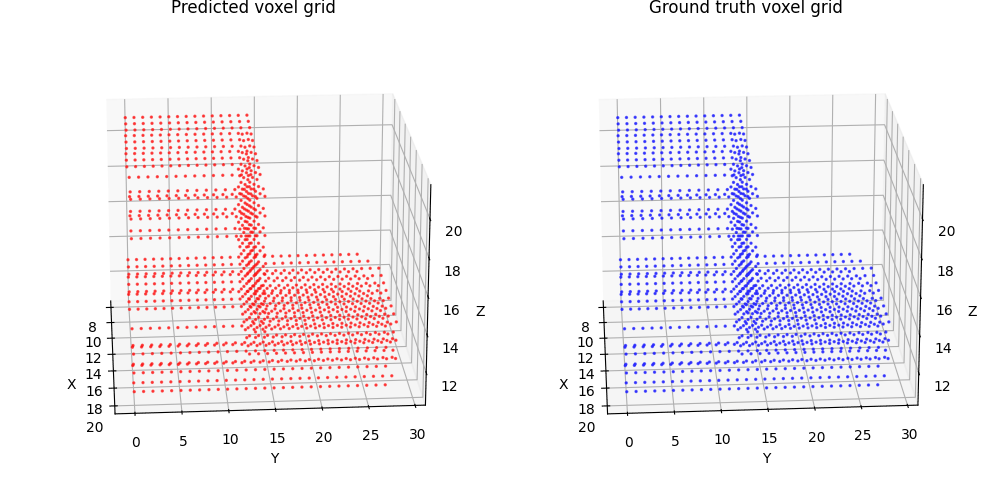
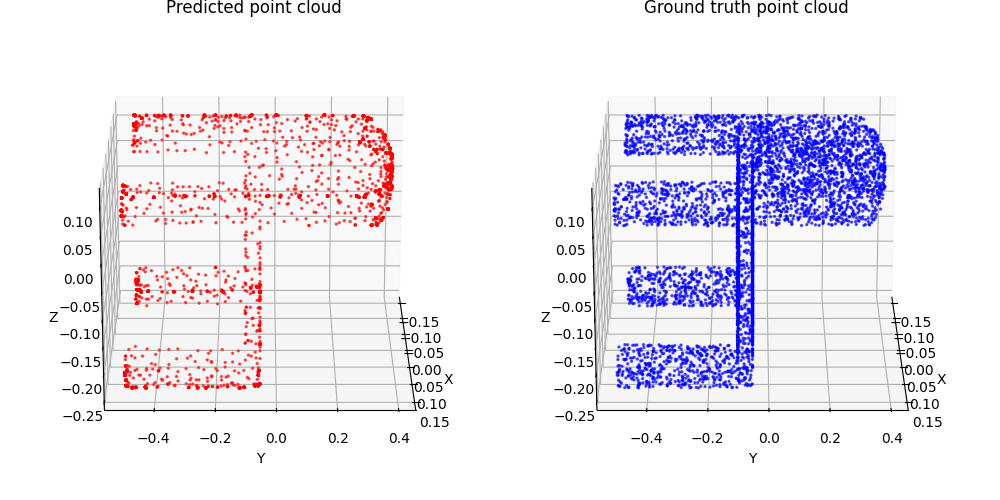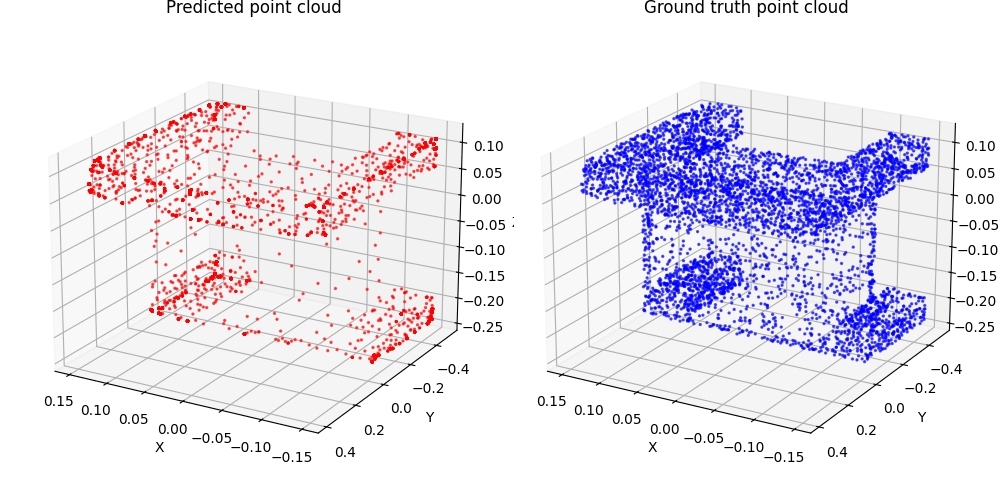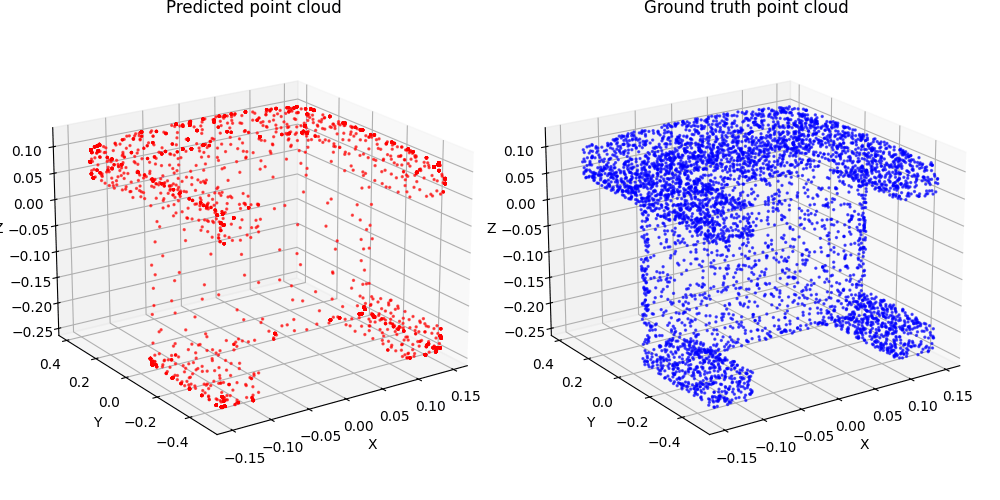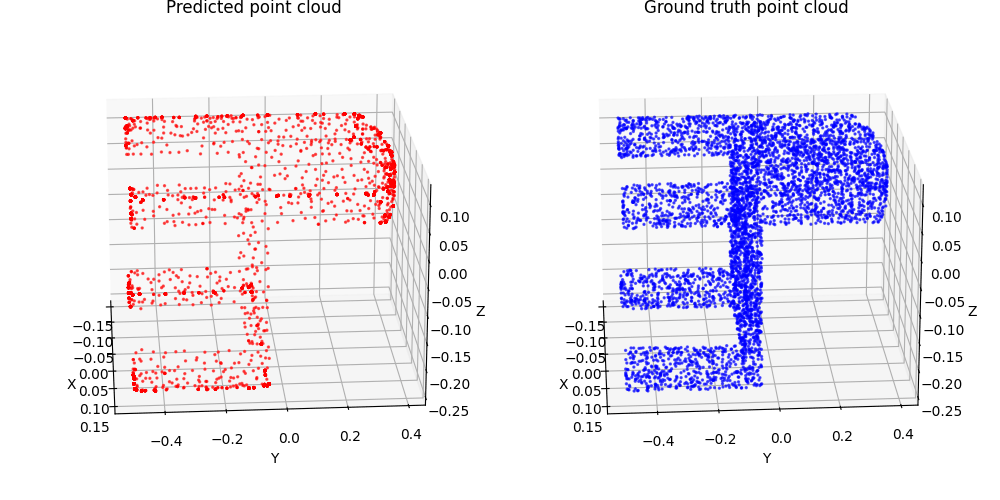
1.2. Fitting a point cloud (5 points)
1.3. Fitting a mesh (5 points)
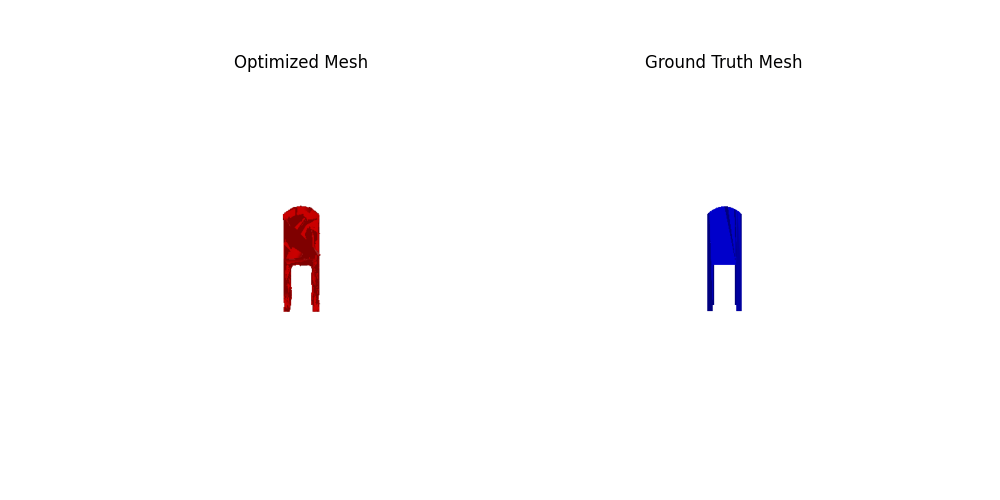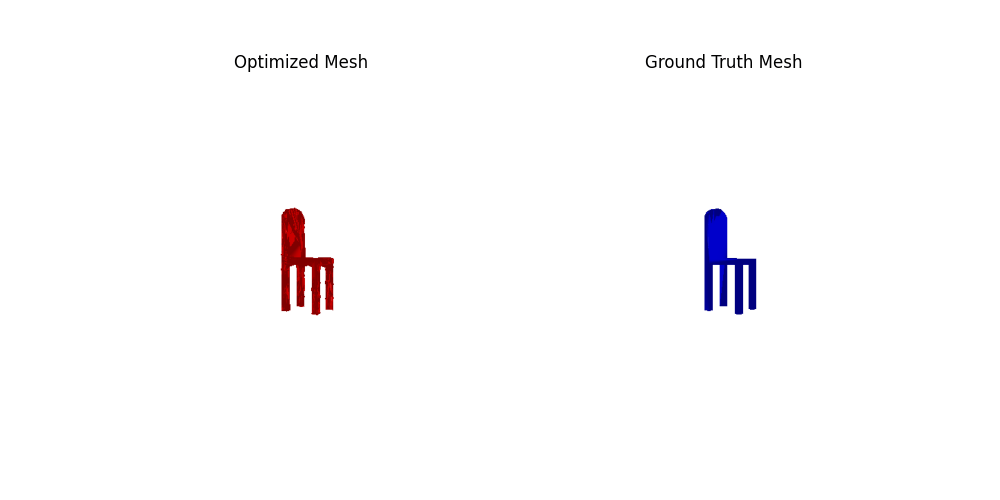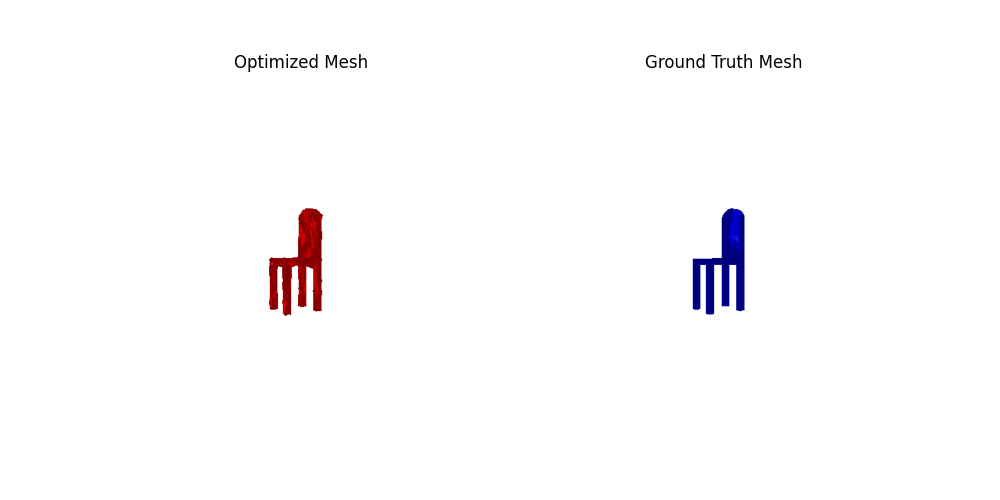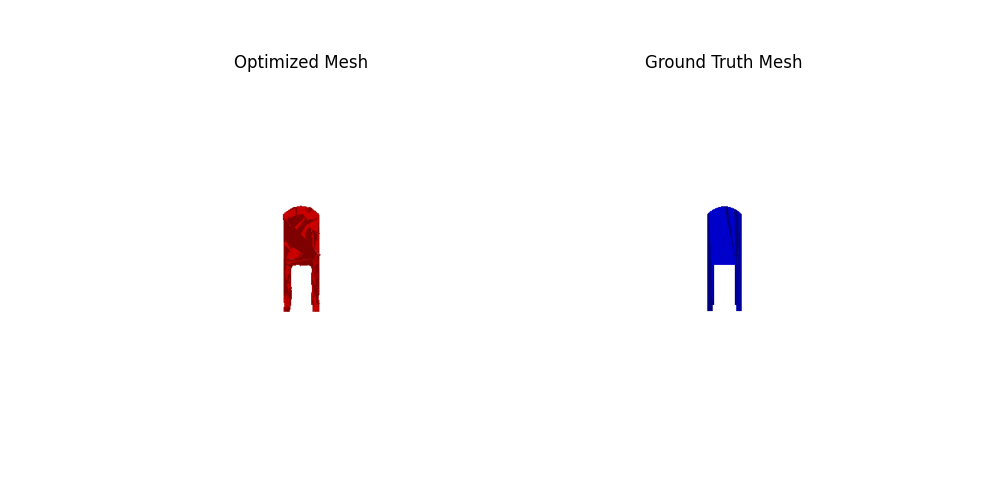
2. Reconstructing 3D from single view
2.1 Image to voxel grid (20 points)

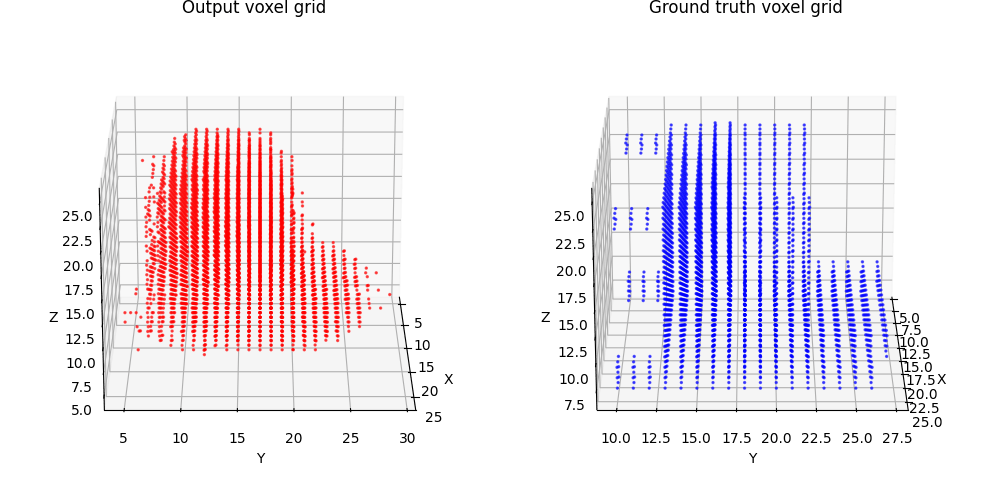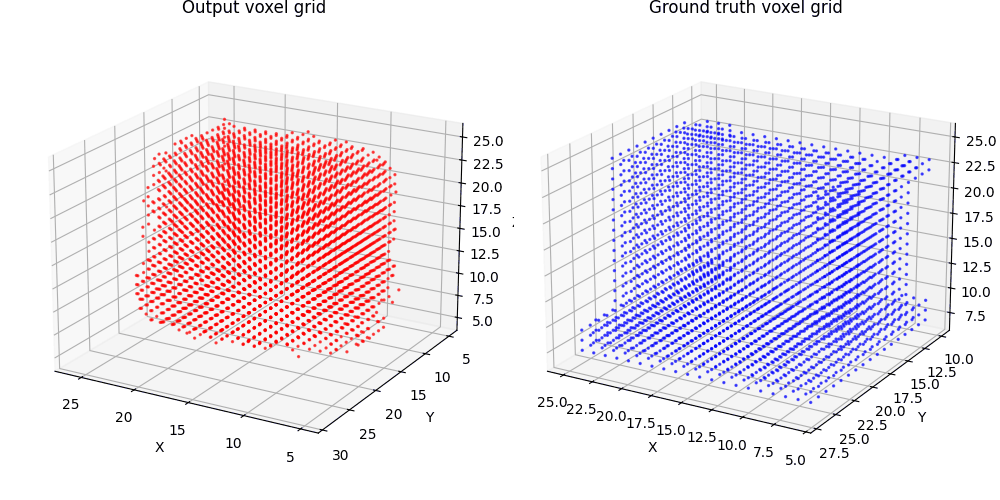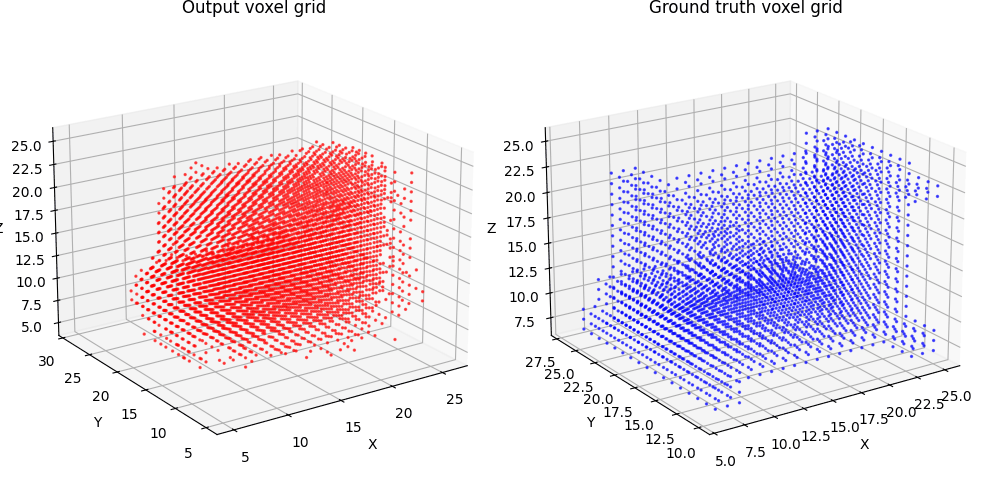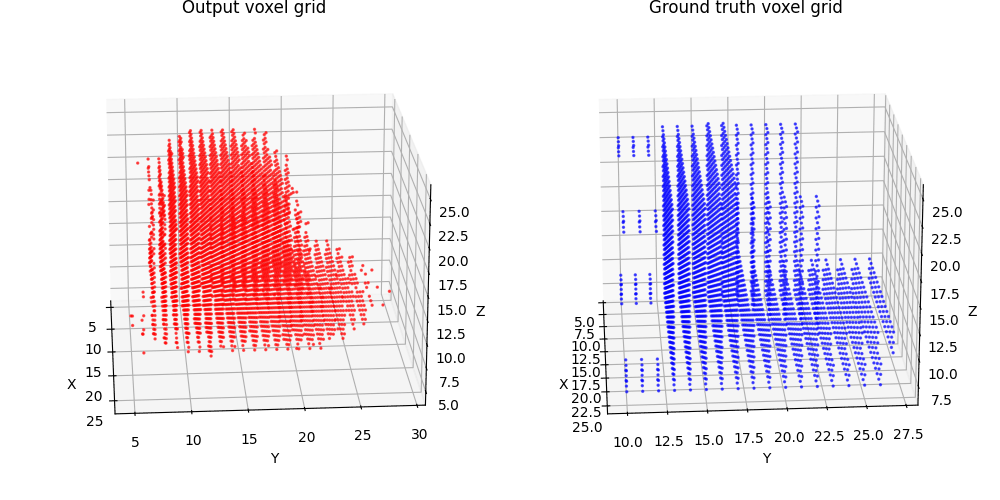


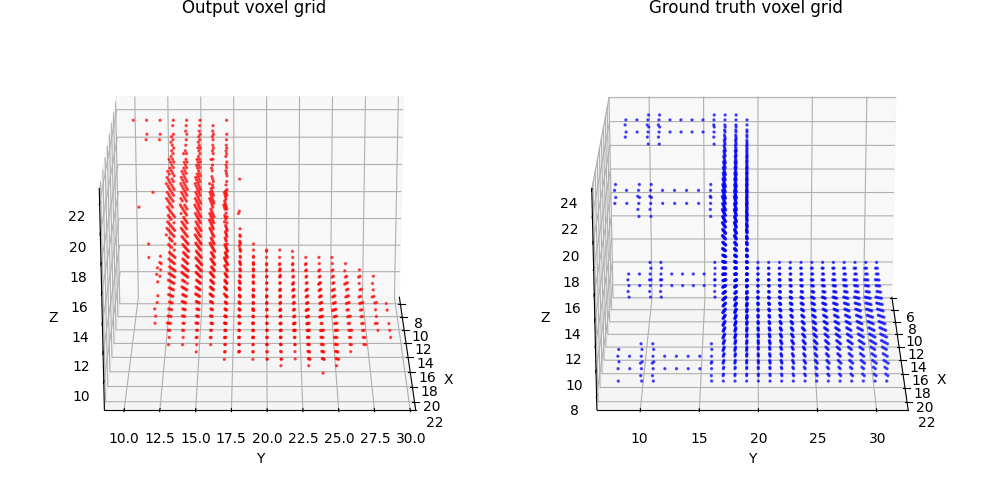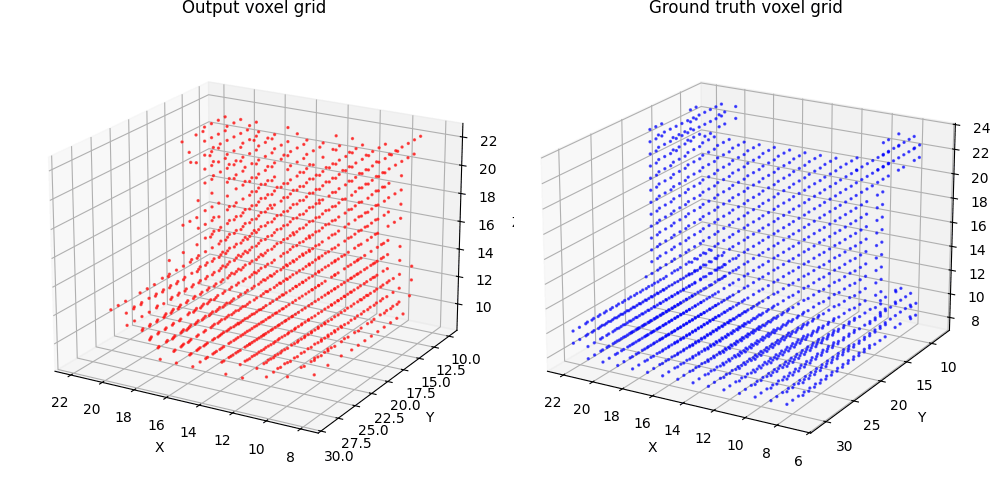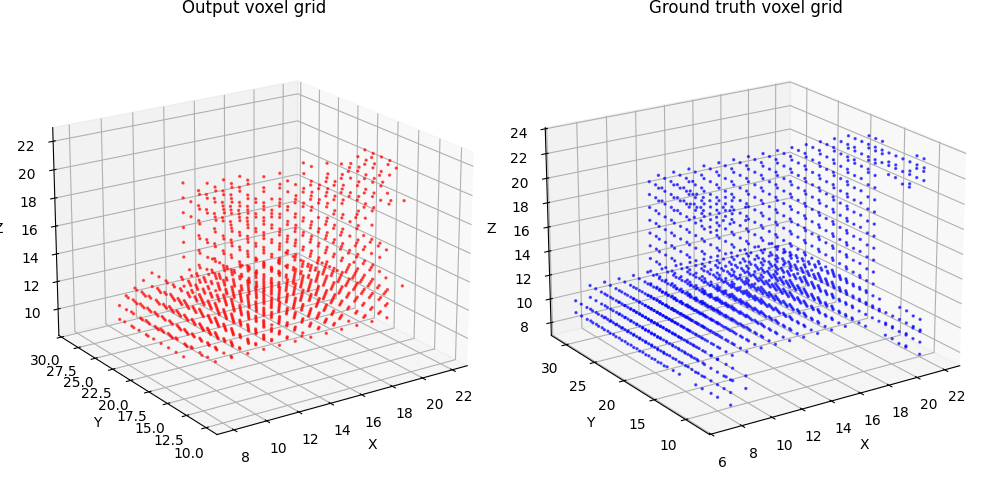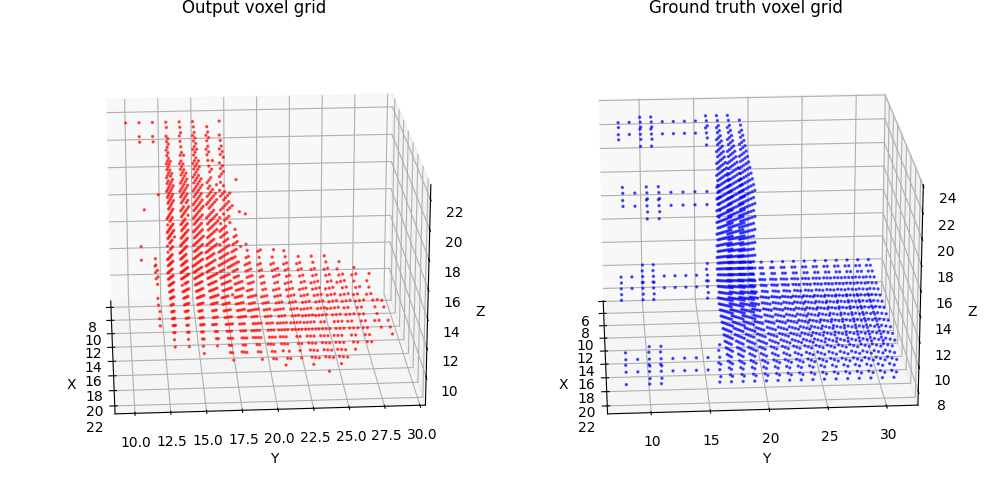
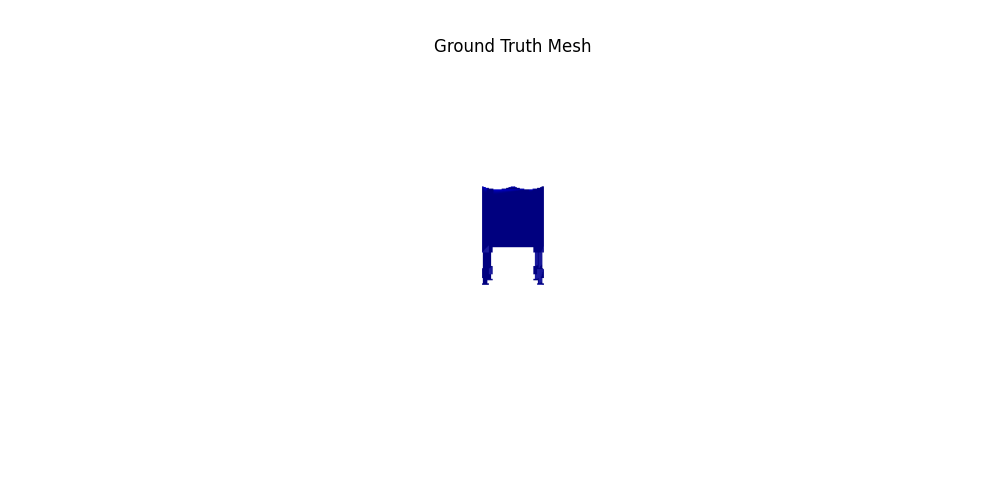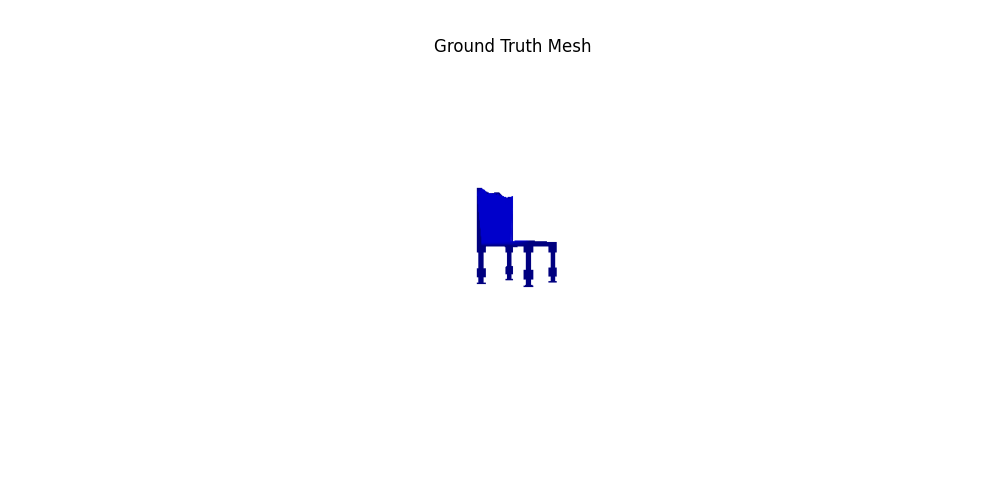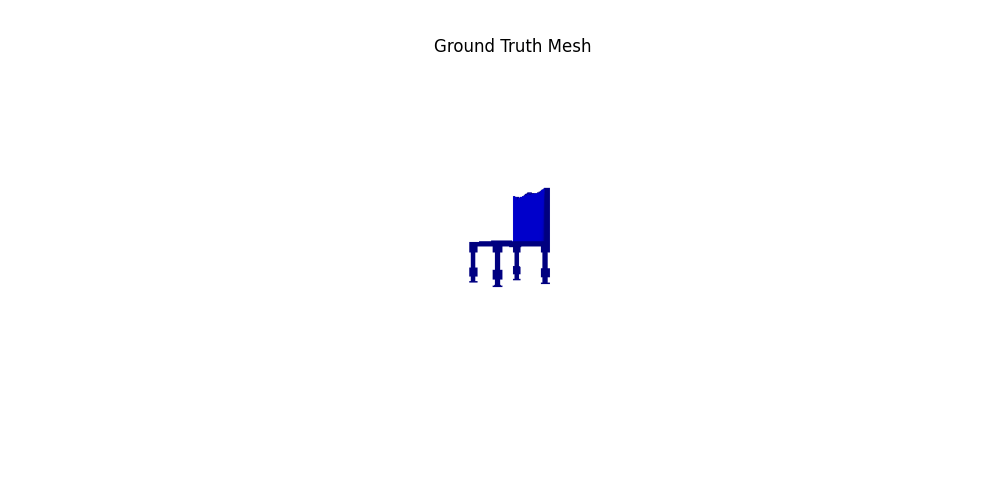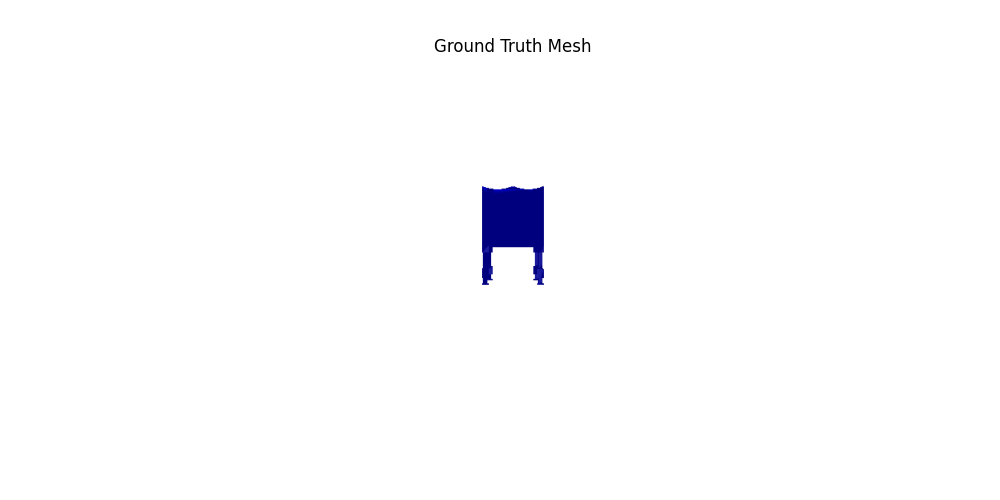

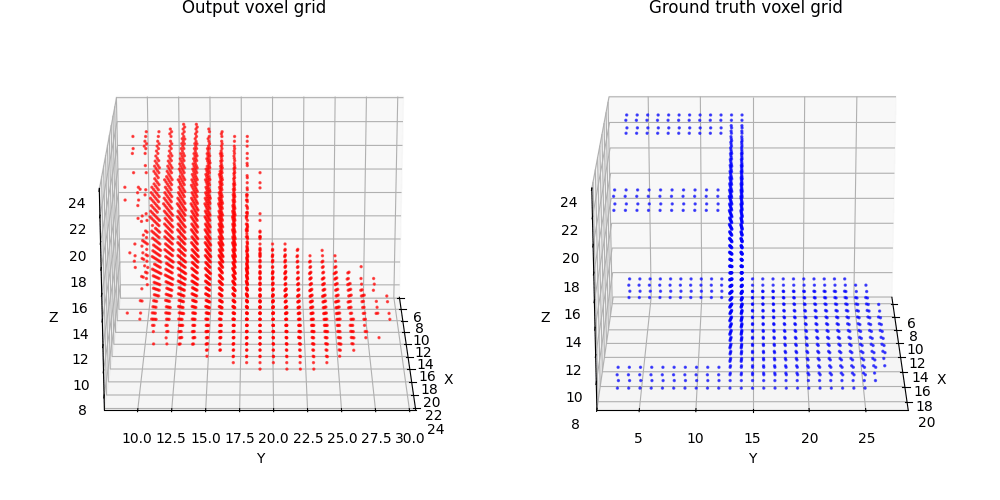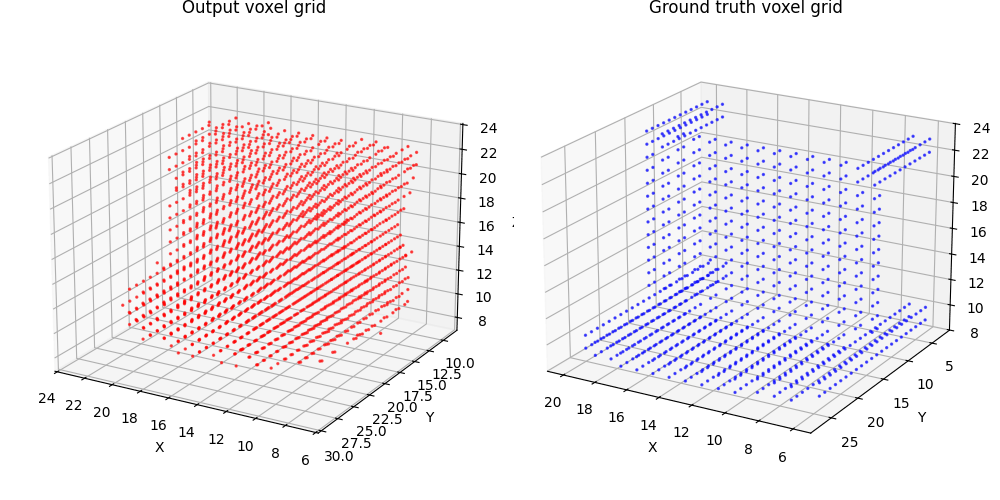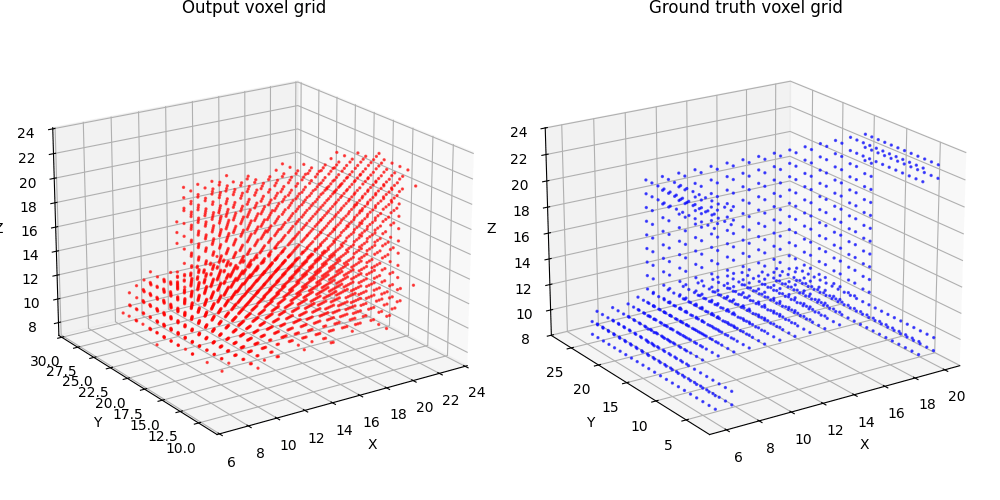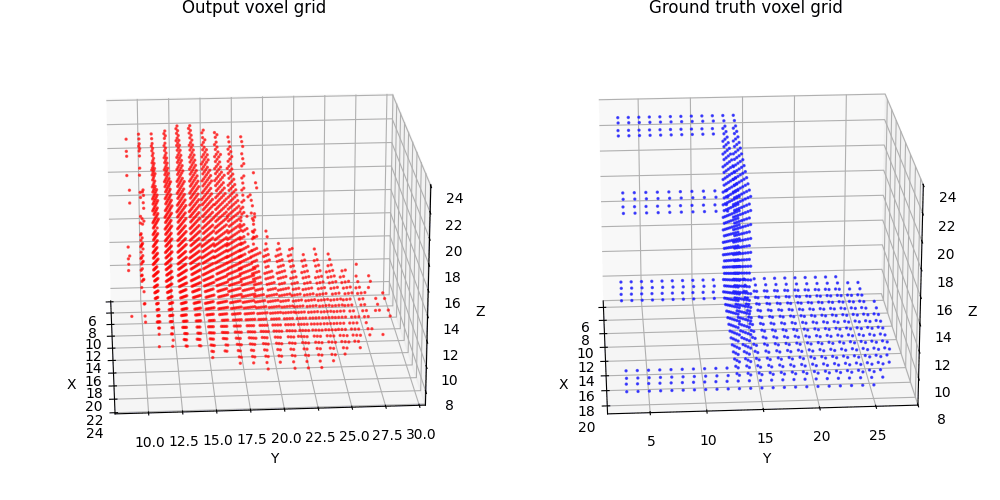

For voxel training, I modified the weight of loss a bit to emphasize the positive voxels, as they are sparse.
2.2. Image to point cloud (20 points)

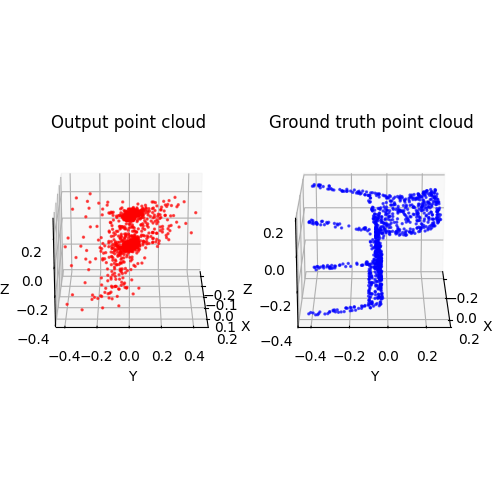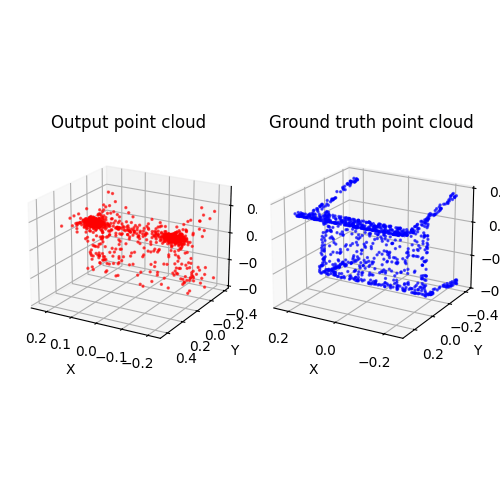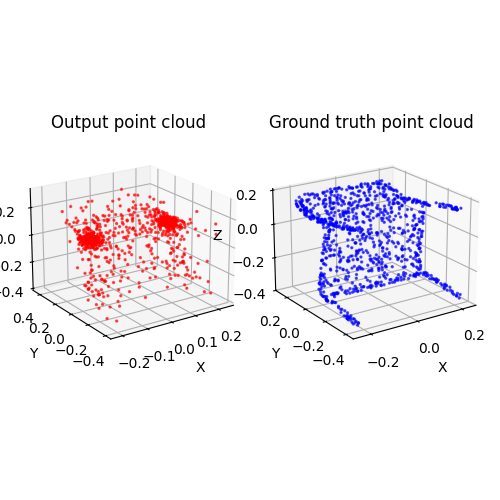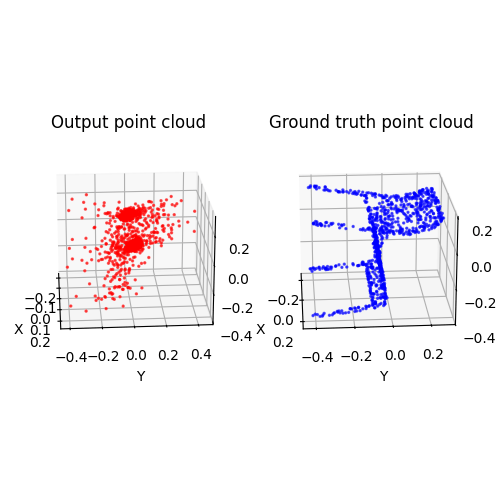

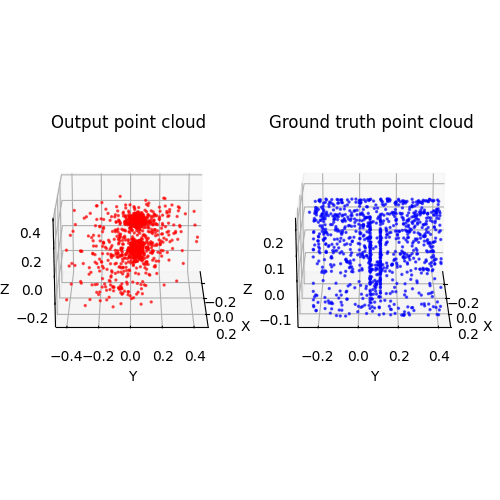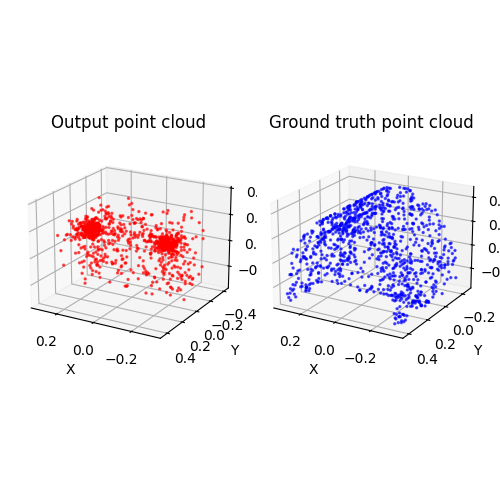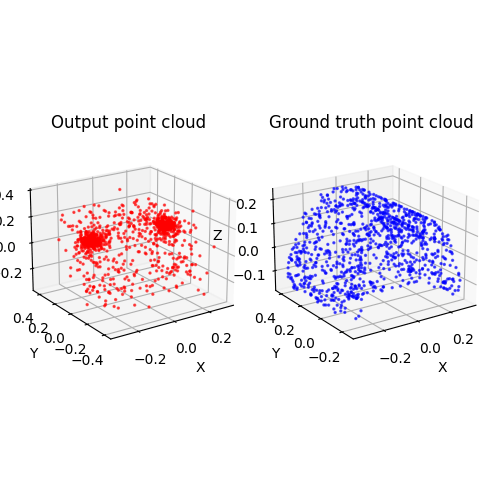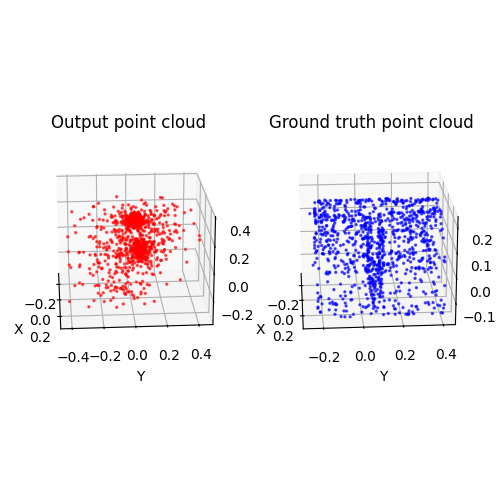

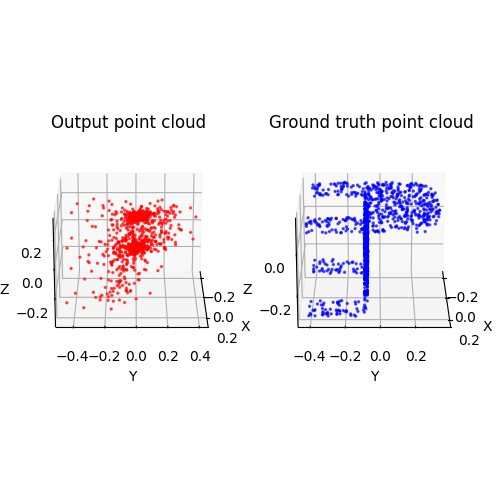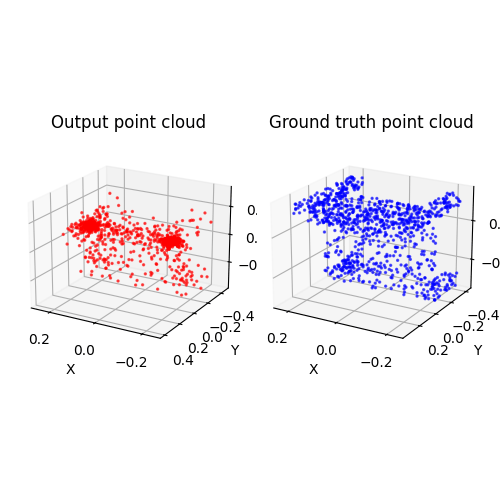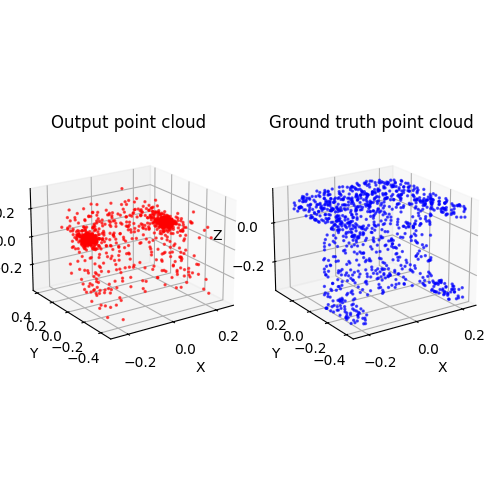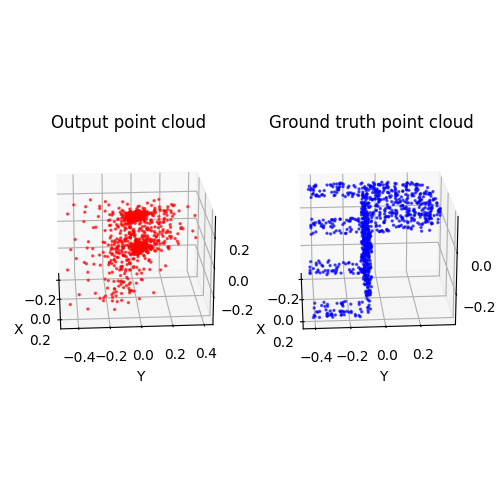

2.3. Image to mesh (20 points)



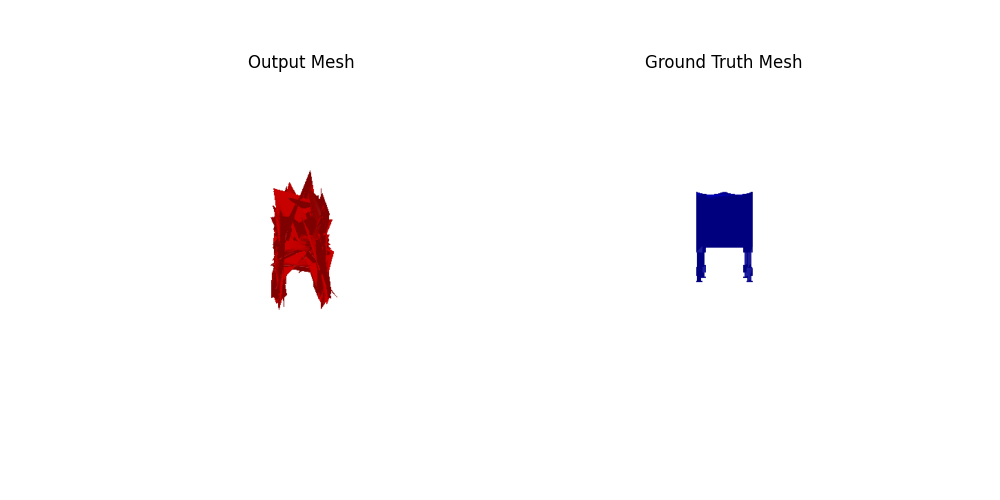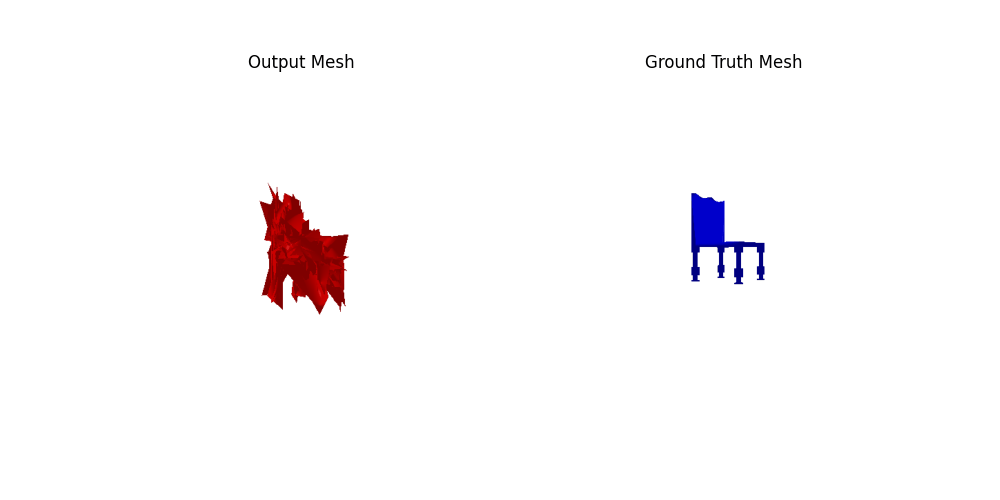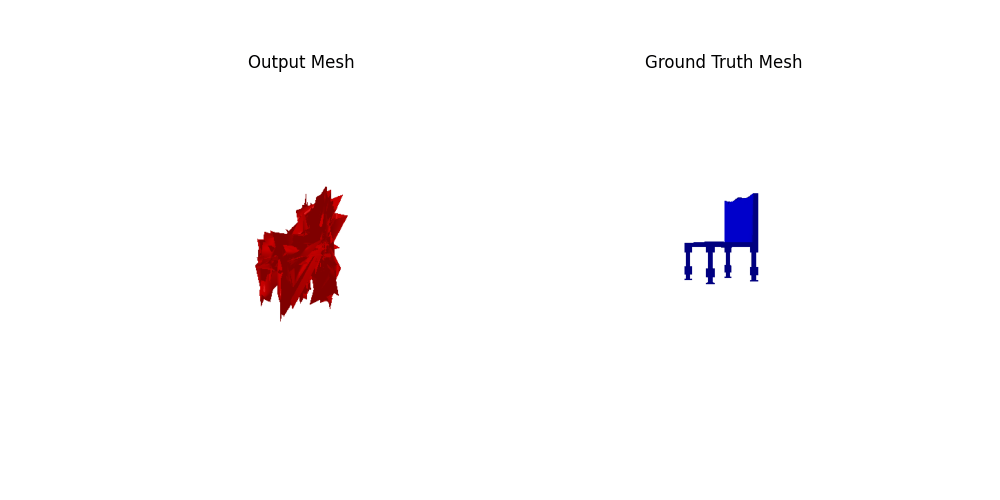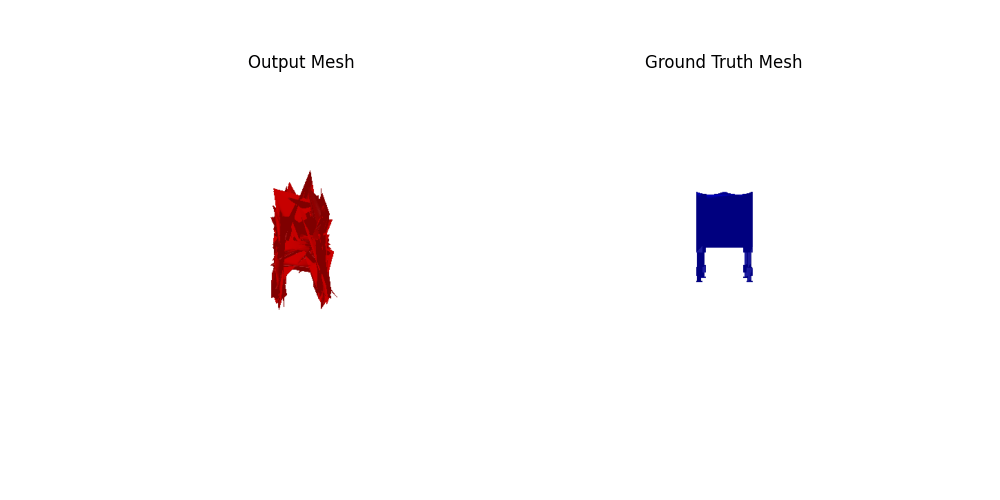


2.4. Quantitative comparisions(10 points)
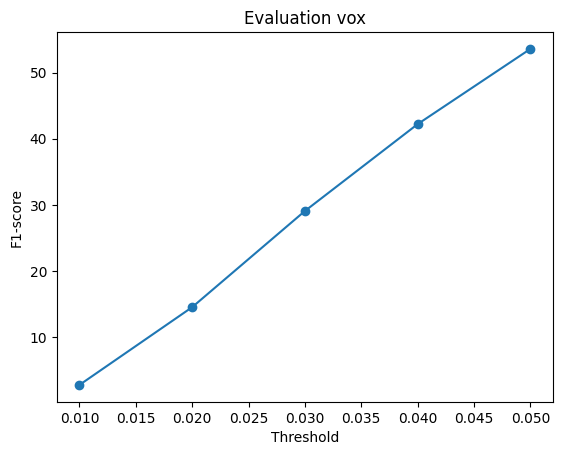
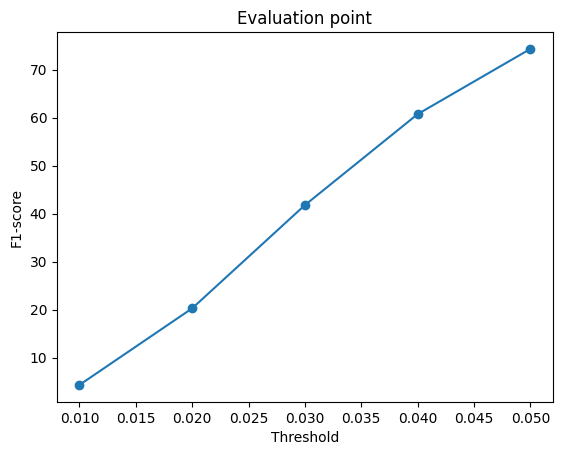
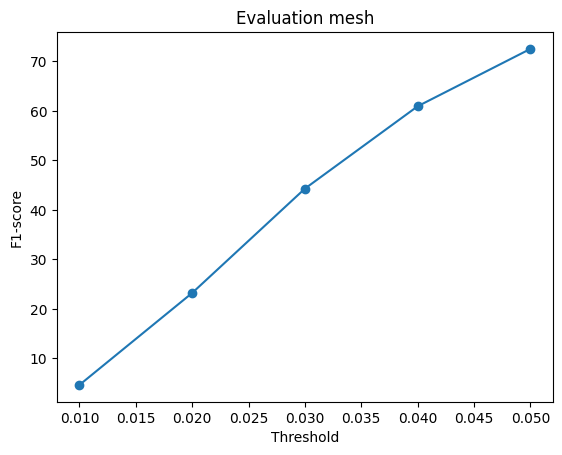
Among 1-3, the pointcloud has the most faithful reconstruction. However, it still suffers in rare shape cases.
2.5. Analyse effects of hyperparams variations (10 points)
Cube init

Sphere (4 subdivisions) init

Sphere (2 subdivisions) init
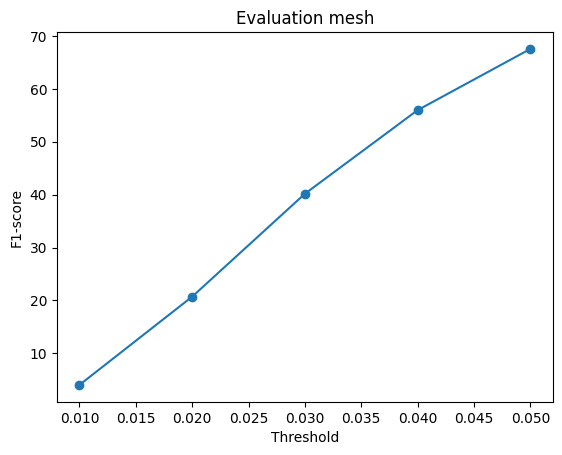
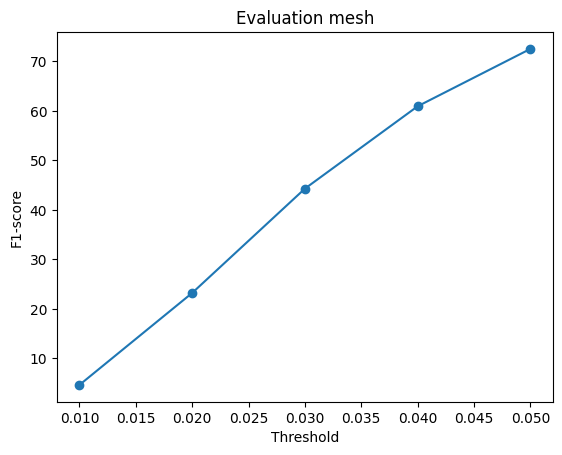
Comparing the initialization using icosphere and cubes(with roughly the same number of faces), the result of the cube init is slightly better. Comparing the icosphere init using 4 or 2 subdivisions, the results of 4 are better (4%+). The number of faces seems more dominant than the initialization shape in this experiment.
2.6. Interpret your model (15 points)

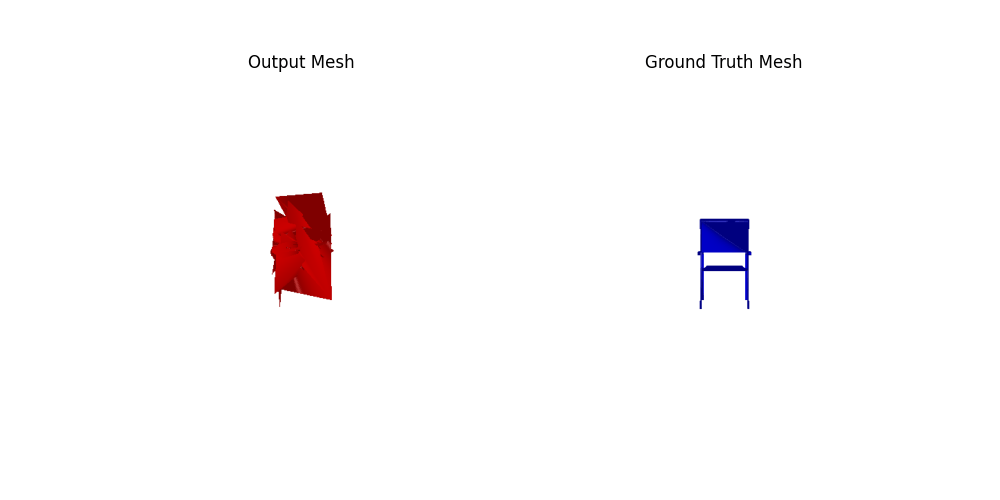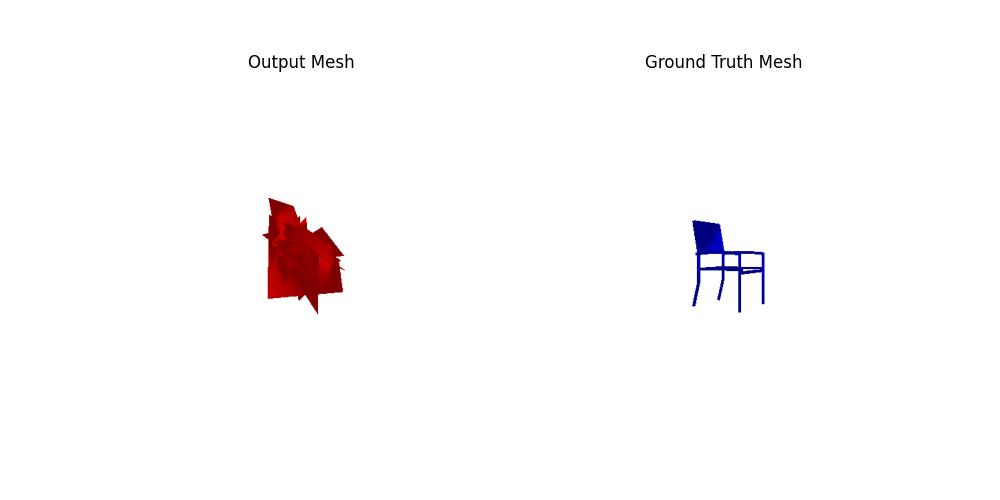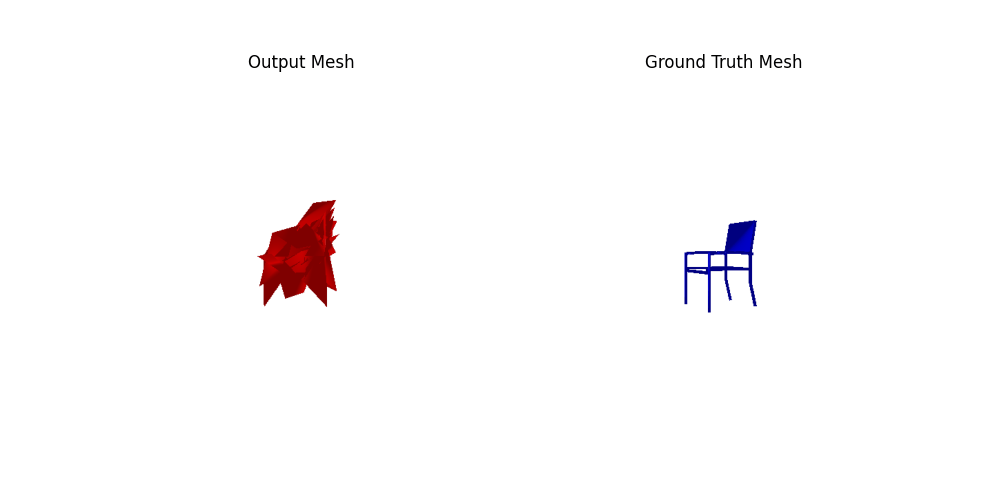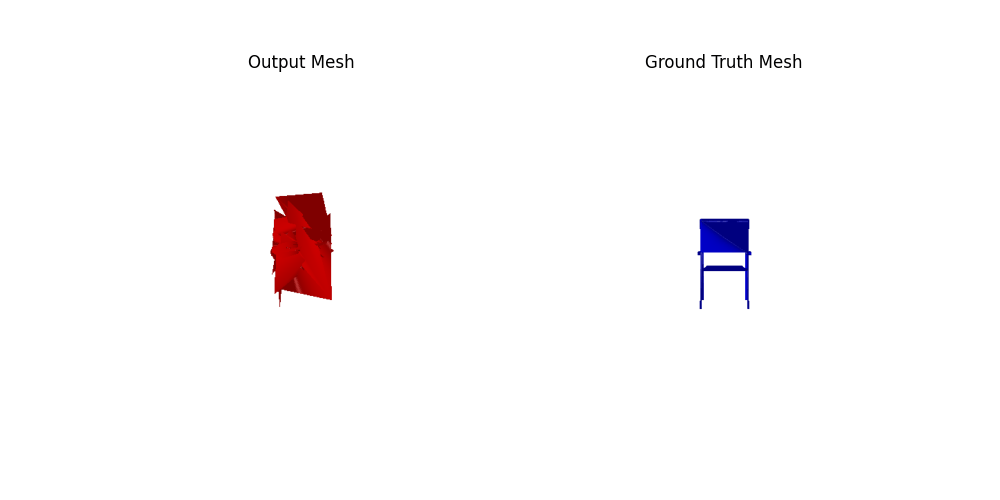
Overlap 2 meshes to see the reconstruction fidelity.
3. Exploring other architectures / datasets. (Choose at least one! More than one is extra credit)
3.2 Parametric network (10 points)
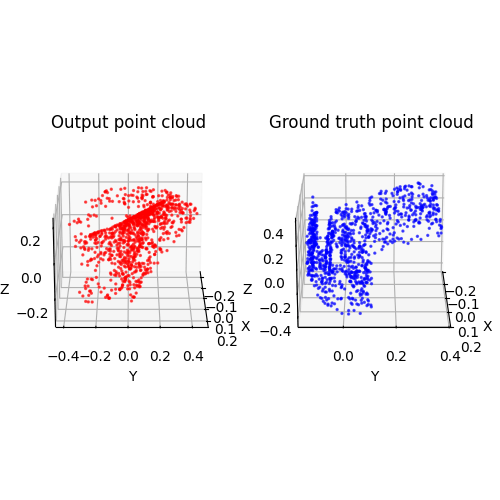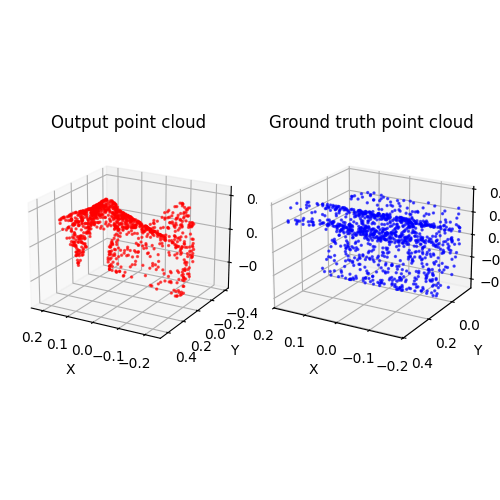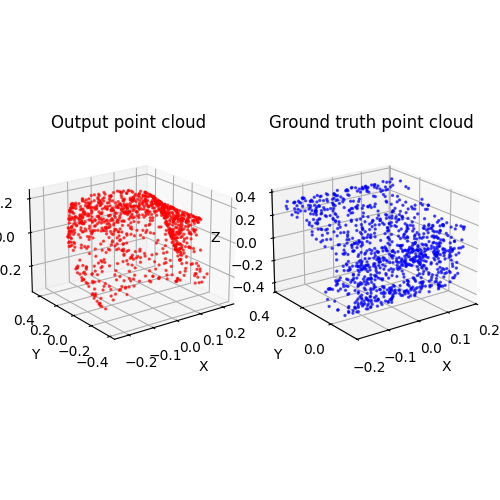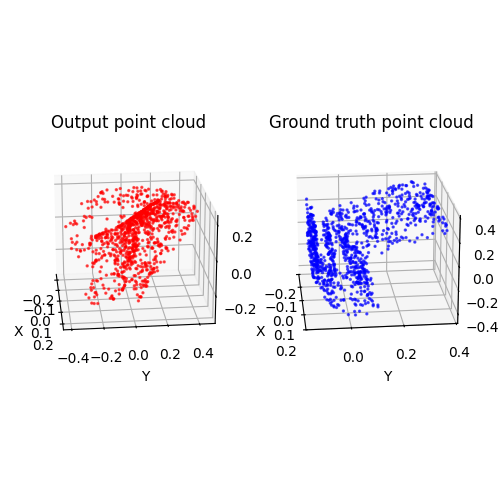
I'm trying to implement a 2D (uv) to 3D (xyz) network. The UV is uniformly sampled from a plane, so the network is a warping function that 'warp' the plane to 3D shape, represented by pointcloud. We use chamfer loss to train the network.One thing is that we try to use one warping function to operate on various chair shape. This degrades the performance and make the loss hard to converge (at least to a low enough value). Train on a specific object or introduce additional conditions while training on one class of object (like image feature) would be better.