|
|---|
| To begin with, oxidation is a process where an atom loses electrons. Reduction is the exact opposite. Together, they are called oxidation-reduction, or redox. Oxidation causes rust because the air takes away electrons from the metals that do not have protection from rust. The chemical formula of rust is Fe2O3.nH2O (or iron + water + oxygen = rust) . Electrolysis is the flow of electrons. Everytime a redox reaction occurs, electrolysis takes place. However, electrolysis can be stopped by galvanizing certain objects, like metal. Moving on, some redox reactions are very harmful to the environment, like corrosion (where rust is made on metal again and again until all of the metal has disentigrated). Redox can produce water by oxidizing hydrocarbons using oxygen. Oxidation and reduction are important in the environment. |
|
| Back to contents |
|---|
Plants and Chemistry |
|---|
| The reason why leaves change colors in witner is actually quite simple. You see, plants have chlorophyll, which makes them green and lets them use photosynthesis. Photosynthesis is their way of making food, and can only work if they have water, carbon, and sumlight. During winter, their is not enough sumlight to use photosynthesis, so the chlorophyll disappears from the leaves, revealing all of the other things in the leaf, like glucose and waste products. Red leaves get their color from glucose, and brown leaves get color from waste. Orange leaves get their color from carotene, and yellow colors come from xanthophyll. Leaves have many colors, and chemistry is involved in it as well. |
|
| Back to contents |
|---|
The Nitrogen and Carbon Cycles |
|---|
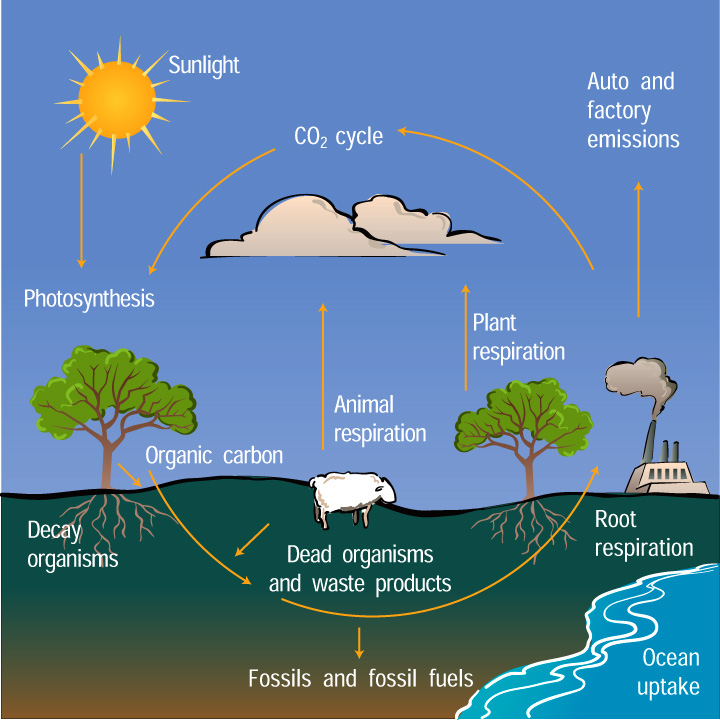
| Nitrogen and carbon are both very important to life on earth. So, nitrogen is important because it makes up proteins, DNA, and chlorophyll. Carbon makes up all organisms on Earth and creates the greenhouse effect. Anyways, nitrogen is absorbed by plants, and is used to make proteins. Then, animals eat the plants, getting the nitrogen. After it dies, other small organisms break down the protein back into nitrogen, which starts the cycle over again. The carbon cycle starts with the plants, who take carbon from the air. Animals then come over and eat the plants. They breath out carbon dioxide while they live. After they die, the dead matter is decomposed by small organisms, which breath out carbon dioxide too. All the carbon in the air is used by the plants again. All this happens in the outdoors. |
|
| Back to contents |
|---|
Chemical Pollution in Water |
|---|
| Water pollution and other things have caused only 2% of the Earth's water to be clean, and about three-quarters of it is ice. Common pollutants can included metals like lead and mecury. Other pollutants include acid rain (caused by nitrogen and sulfer oxides), infections, and landfills. Pesticides will contaminate water, and heat can actually be a pollutant as well. People have, however, found out ways to decontaminate sewage by seting it through a bunch of different filters. Regular water from lakes, streams, or reservoir, is filtered too, to take things out of the water. Those filters remove germs, substances that would give the water taste, odor, and/or color. Much of the clean water we take for granted as clean can start as very dirty and polluted liquid. |
|
| Back to contents |
|---|