Mathematical Model for the HVAC System
Current Model:
Currently, the model used for the control system of the IW is formulated by Siemens. The flow chart below describes the functioning of the model. The model uses the Proportional Integrative Derivative (PID) controller model. In this model, the supply temperatures work towards meeting the set point temperatures for each zone. The difference in the supply temperature and the set point temperatures are treated as the error, and mixing valve helps in eliminating this error by equalizing the supply temperature to the set point temperature.
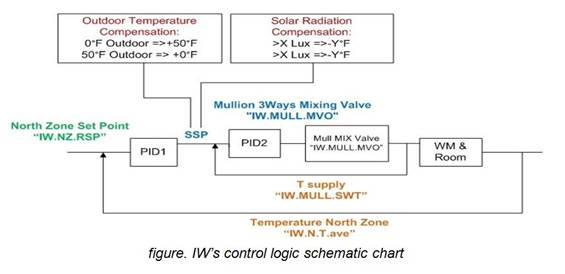
Previous Model:
In the Johnsons control system, the system turns on the basement pump (HWP1 and HWP2) if the average south zone and north zone indoor temperature ((Tsouth +Tnorth)/2) is below the pump set point (60 F) or if the schedule calls for it. The Metasys server also turns on the fourth floor mullion water pump if the average indoor temperature is below the mullion water pump set point (60 F) or if the schedule calls for it. The hot water supply temperature set point is based on the indoor and outdoor temperature, and a comfort weighting factor. The hot water set point equation is:
Thws = (38-To)*foA + (72 – (Tsouth + Tnorth)/2) * fIA +120
Thws - Hot water supply temperature set point
Tnorth & south – indoor temperature of south/north zones
foA & fIA – outside/inside air temperature weighing factors (1)
The steam valve modulates to maintain hot water set point temperature at the outlet of the heat exchanger. The three way control valve before the mullion pump continuously modulates to maintain the mullion surface temperature set point. The mullion surface temperature set point is decided by the equation:
T mullion-s =((Tsouth +Tnorth)/2 + Thws)/2
T mullion-s - Mullion Surface temperature set-point
