Vibration #3: Vibration
in a Saxophone Reed
Introduction:
In this example you
will execute modal analysis of a saxophone reed and find its natural
frequencies.
Physical Problem:
The reed is as
defined below. The model is simpler than a true reed so the general idea
is so determine the behavior of a closely similar physical model using
the exact material model. The frequencies will be similar. It is firmly
attached along the back 3cm of its length.
Problem Description:
∑
The
reed has dimensions as explained in the diagram.
∑
The
reed is made of bamboo with a Young's modulus of 28.8e6, Poisson's
ration of 0.3, and a density of 1158 kg/m2.
∑
Assume the reed is connected to the mouthpiece and is
fixed in all degrees of freedom. The reed is solid and has material
properties that are constant and isotropic.
∑
Objective:
To
determine the natural frequencies of vibration
To
generate animations of these vibrations.
Figure:
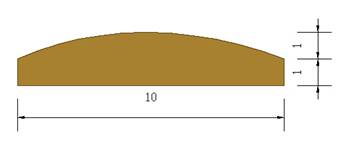 (mm)
(mm)

IMPORTANT:
Convert all
dimensions and forces into SI units.
∑
Create the cross-sectional area of the reed using key
points to define the 4 edges of the rectangular solid portion, and one
key point in the middle of the arc in the top of the reed to map a
spline.
∑
Set the Material Properties of the reed. (Hint: Elastic
Modulus, Poisonís Ratio, and Density are important to define
∑
Define two types of elements: Quad 4node 42 and Brick
8node 45.
∑
Use the mesh tool to set the Global Mesh size to 0.00025
and mesh the cross-section using the 2D mesh set from element type 1.
∑
Extrude the shape using the second element type (Brick
8node) 8cm in the Z direction. (Donít mind the warning. If we were using
a full version of ANSYS, we would be able to choose SOLID95 instead,
which would extrude without error.)
∑
Set the Boundary Conditions. (First unselect the Plane 42
elements used in the 2d area mesh. Next, apply the DOF constraints to
the end of the reed such that 0.03m of the reed is unable to move.
Finally, reselect all nodes.)
∑
Solve for the natural frequencies of vibration of the
vocal chords. (Use a modal analysis using the Block Lanczos Mode
Extraction method and solve for 5 modes.)
∑
List the nodal frequencies of vibration for the vocal
chords.
∑
From the results obtained, read the first set, then
animate the mode shape using 30 frames with a 0.25 second time delay
between frames. Be sure to show the DOF Solution with both the Deformed
and Undeformed Edge. This will properly demonstrate the vibration
patterns in the vocal chords.
∑
Plot the nodal solutions to use as screenshots and compare
with the answers below.
(These are the
results you should expect:)
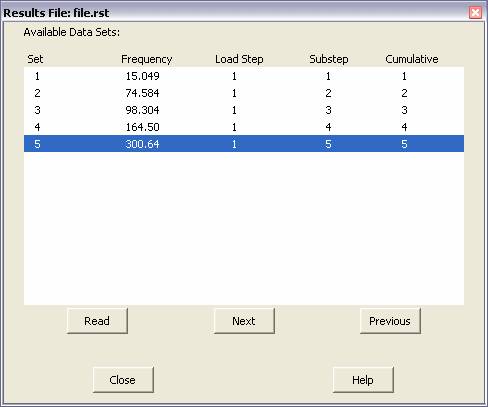
(Modes of vibration:)
First
 RIGHT
RIGHT
Second
 TOP
TOP
Third
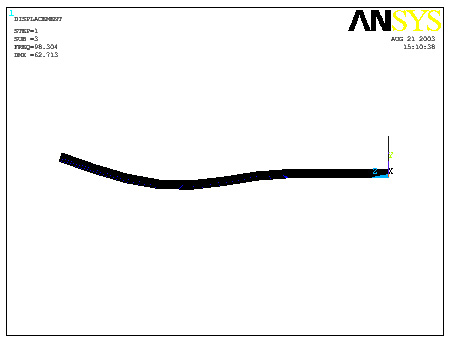 RIGHT
RIGHT
Fourth
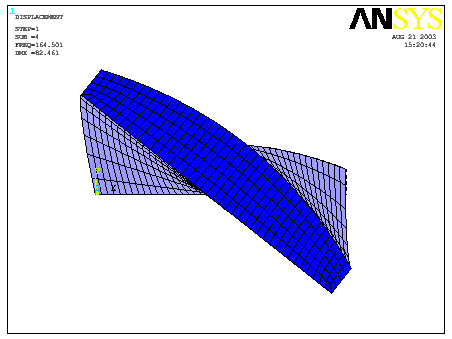 FRONT
FRONT
Fifth
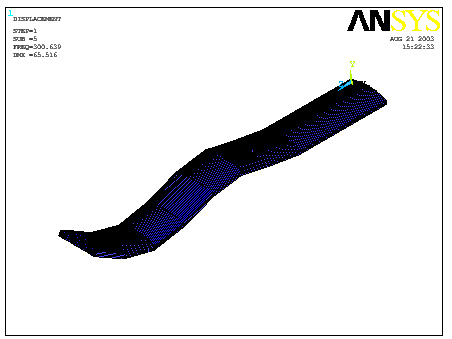 ISO
ISO