- How many references you must change to delete a node from the middle of a singly linked list?
a) 1
b) 2
c) 3
d) 0
- Why one might choose to use a singly linked list instead of a doubly linked list?
a) Insert is not efficient for a doubly linked list
b) A doubly linked list has a fixed size
c) Memory usage is a big concern for you
d) Remove takes constant time for a singly linked list
- Given a doubly linked list where each node has two references (prev and next):
one that points to a previous node and another to a next node:
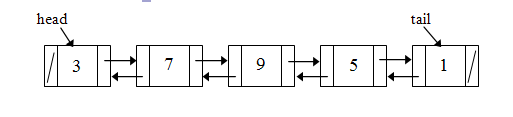
Assuming the linked list above, provide the output for the following code fragments.
The list is restored to its initial state before each line executes:
a) _________ head.next.next.next.data;
b) _________ head.next.next.prev.prev.data;
c) _________ tail.prev.prev.prev.next.data;
- Given an array and a singly linked list. Which of these data structures uses more memory
space to store the same number of elements? Explain your answer.
- Given a singly-linked list of unknown size. Describe in a few sentences (in English, please)
how to find the middle element of the list without counting all nodes.
- What changes do you need to make to a linked list in order to have a constant time access
to the last node?
- An alternative to a standard deletion strategy is known as lazy deletion.
When deleting elements from a singly linked list, we delete them logically but not physically.
This is done by marking the node as deleted (using a boolean value). The numbers of deleted and
not-deleted elements in the list are kept as part of the list. If at some point the number of
deleted elements is equal to the number of not-deleted elements, we traverse the list and
delete all "lazily deleted" elements. Discuss the advantages and disadvantages of this scheme.
- Given a doubly linked list where each node has two references (prev and next):
one that points to a previous node and another to a next node.
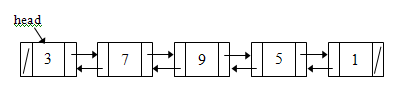
Write the statements to insert a new node
Node toInsert = new Node(6);
containing the 6 between the node with the 5 and the node with the 9.
You do not need to write the whole method but just the statements to make the connections.
- Implement a Java method
public void removeAllMatchingItems(AnyType keyItem)
that removes each and every item equal the keyItem from a
singly-linked list. The list is not changed in any other way - if the requested item is not
contained within the list, the method leaves the list in its prior condition
You assume the LinkedList class given in lectures.
- Given a sorted singly-linked list, where the head contains the smallest element
Implement a Java method
public void insertInOrder(Comparable keyItem)
that creates a new node and inserts it in-order into the list.
You assume the LinkedList class given in lectures.

