pH Titration
Model reaction:
HA <=> A- + H+
Acid dissociation constant: Ka = [A-][H+]/[HA]
- The Henderson-Hasselbalch equation is:
pH = pKa + log([A-]/[ HA]), where
- pH = the measured pH, (-log[H+]);
- pKa = -logKa;
- [HA] = the concentration of the acid, and
- [A-] = the concentration of the conjugate base.
The titration of 100 mL of carbonic acid with 1.0 M NaOH is shown below. You are asked to determine
1) the concentration of the acid and
2) the pKa.
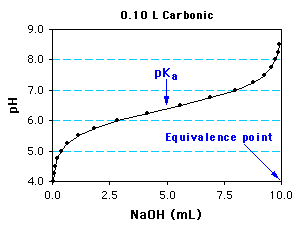
1) The equivalence point is approached as mol NaOH approaches the mol carbonic acid in solution (10 mL NaOH = 10 mmol).
Therefore the acid concentration, [Acid] = 10 mmol/0.10 L = 0.10 M.
2) At half the volume of NaOH required to completely titrate the acid (5.0 mL above), [HA] = [A-], and pH = pKa = 6.4.
11.14.02
