Distances:
- Highlight:
1. Micelle Regions - a.
Polar Head Groups. - b.
Hydrophobic Tails. - c. H2O:
Hide. Add back. - b.
- 2. Single DPC Molecules.
-
DPC 1 (Slab Mode) DPC 1 contacts, yellow. Contacts, Spacefill.
Contacts, Sticks (+dots). -
DPC 2 (Slab Mode) DPC 2 contacts, yellow. Contacts, Spacefill.
Contacts, Sticks (+dots). -
DPC 3 (Slab Mode) DPC 3 contacts, yellow. Contacts, Spacefill.
Contacts, Sticks (+dots).
The theoretical model shows 54 molecules of dodecylphosphocholine (DPC) and about 1200 H2O molecules. Each lipid has a polar head group (phosphocholine, Ball & Stick) and a hydrophobic tail (dodecyl = C12, Sticks). The waters are Sticks. The coloring of all molecules is CPK. The validity of this model is supported by experimental data on the size and shape of similar micelles in solution.
The numbered "Highlight" buttons above display details of the micelle structure. The following paragraphs briefly describe the displays.
1. Micellar Regions.
The polar polar head groups are shown Spacefill. H2O surrounds and penetrates all of the spaces in the headgroup region.
The hydrophobic tails are shown Spacefill. H2O is excluded from this entire interior volume. The hydrocarbon chains vary in their individual conformations (e.g. trans/gauche configuration at each carbon-carbon bond), but adapt so as to fill all of the interior space.
Toggle between "Hide" and "Add back" H2O for these displays and those below.
2. Single DPC Molecules
The close-ups of DPC molecules 1-3 are shown Spacefill; the rest of the micelle is Sticks. Deselect Slab Mode (under Options) if the highlighted region moves out of view.
The "DPC contacts" show 10-15 H2O's that make favorable H-bond or ion-dipole interactions (<3.5 Å). Neighboring DPC molecules that are within 4.0 Å of each DPC are thicker Sticks; the atoms on each that can make favorable van der Waals interactions are colored yellow. The "contact atoms" can be displayed Spacefill or Sticks (+ Dot surface).
Note: In contrast to protein crystal structures where interior atoms are relatively fixed and the "knob-into-hole" packing is very similar in each molecule, the micelle interior is highly dynamic, i.e. each lipid may have 4-8 contacting neighbor lipids at any instant, but these partners change several times every nsec on average.
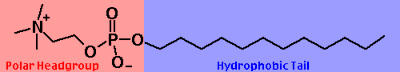
Chemical Structure of Dodecylphosphocholine (DPC)
DPC is a synthetic phosphodiester. The phosphoric acid group has ester bonds between 1) choline, (CH3)3N(CH2)2OH, and 2) dodecyl (or lauryl) alcohol, CH3(CH2)11OH.
[Put the mouse over the image to show the complete chemical structure.]
"Group Colors" uses the RasMol "rainbow color scheme" to distinguish 13 groups of DPC molecules from DPC 1 to DPC 54. The final display shows the head groups as thin Sticks and the tails as thicker "Licorice Sticks".
Page Top ![]()
The structure and its calculated dynamic properties are described in D. P. Tieleman, D. van der Spoel, H.J.C. Berendsen (2000) "Molecular dynamics simulations of dodecylphosphocholine micelles at three different aggregate sizes: micellar structure and lipid chain relaxation" J. Phys. Chem. B 104:6380-6388. Abstract.
Dr. Tieleman's Project Page at the Univ. of Calgary describes micelle structures in more detail.
See also Fig. 2.3 in Campbell for a schematic micelle structure.