Cooperative Binding
Dissociation constant: Kd = [P][A]nH/[PAn]
Fractional occupancy: Y = [A]nH/Kd + [A]nH
- The Hill equation is derived from the expressions for Kd and Y. In logarithmic form:
log(Y/1-Y) = nHlogA - logKd
, where
- nH = the Hill coefficient (maximum slope of the Hill plot);
- A = [A]free;
- Kd = the dissociation constant.
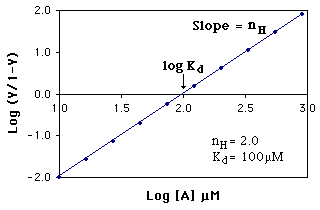
The cooperative binding parameters are determined from the slope and the X-intercept of a Hill Plot as shown below:
For a few of the graphs, you will need to recall that log(2) = 0.3.
12.2.99
